
Experiment 4
Whose shoes were at the scene of the crime?
Experiment 4
In this experiment you will find out which suspect or suspects had soil from the scene of the crime on his or her shoes by using cabbage juice as a pH indicator.
Watson observed that the soil from the suspects’ boots when mixed with cabbage juice exhibited three different colors.
- Mr. Plover and Mr. Mopster’s samples turned red.
- Mr. Grazzbur and Ms. Blodderbum‘s turned a greenish blue.
- Ms. Crowler’s didn’t change color at all, but remained purple.
Watson, Crick and Rosa unfortunately spilled their cabbage juice and now it is up to you to find out what color cabbage juice will exhibit when mixed with a base! From the story, the soil from the scene of the crime is known to be a base.
I] Hypothesis
Cabbage juice will consistently exhibit one color when mixed with an acid, another color when mixed with a base, and another color when mixed with neutral pH substances.
II] Materials needed
- 1/3 of a head of red cabbage
- 5 small clear glasses or cups
- a bowl of hot water from the tap
- clear tape and a permanent marker
- a sieve, or pasta strainer
- some bases like baking soda and dish soap
- some acids like lemon juice and white vinegar
- a neutral pH liquid like tap water
- (Tap water is usually not a perfect neutral pH. However, for this experiment most tap water will work just fine. If you want to be certain that your water has a neutral pH use distilled water)
- some small clear cups or glasses
III] Procedure
- Break up about 1/3 of a head of red cabbage into tiny pieces.
- Soak the cabbage pieces in hot water for at least an 2 hours. Best if you leave it overnight.
- Separate the cabbage juice from the cabbage by carefully pouring the juice into an empty glass. You may want to use a sieve to keep out any cabbage pieces.
- Prepare bases to be tested. Pour a small amount of dish soap in a glass (about a tablespoon (15 milliliters)). In another glass mix about a tablespoon of water with a teaspoon (5 milliliters) of baking soda. Using tape and a marker, label these glasses base.
- Prepare your acids. Pour a small amount (about a teaspoon (5 milliliters)) of lemon juice into a glass. In another glass pour in about a tablespoon (15 milliliters) of white vinegar. Using tape and a marker, label these glasses acid.
- In another glass pour in a small amount of tap water (about 2 tablespoons (30 milliliters)). Using tape and a marker, label this glass neutral pH.
- Pour about 2 to 3 tablespoons (40 milliliters) of red cabbage juice into each of your labeled glasses. Mix each solution carefully and observe the color changes. Answer the question below.
Now that you know what colors acid, base and neutral liquids will exhibit when mixed with red cabbage juice, are you able to deduce which snodlops’ shoes might have been worn at the scene-of-the-crime? Remember the soil at the scene of the crime comes from a limestone cave and limestone is basic.
What is pH?
pH is used to measure whether or not a solution is an acid, an base or neutral. A neutral solution is neither an acid nor a base. Pure water is a neutral liquid.
What is an acid?
Most of us our familiar with term acid. For years Hollywood has shown us some extreme examples of acids. You might have seen a movie in which a bottle of acid drops, breaks and burns a hole in the floor. Indeed, very strong acids can burn and should be handled with care. Some acids are so strong that just smelling them can burn your nose! However, we are surrounded by many other weaker acids, which are safe to handle. Some examples of acids include: lemon juice, orange juice and vinegar. Red cabbage juice will turn into a different color when mixed with an acid.

What is a base?
Strong bases can be just as corrosive and dangerous to handle as strong acids. Some drain cleaners that you use to dissolve clogs are strong bases. However, like acids some bases are weak bases and are safe to handle. Baking soda and dish soap are two bases that are safe to touch. Red cabbage juice will also turn colors when mixed with a base. This color is a different color than the color it changed into when mixed with an acid.
Explaining the pH scale.
The scale is from 1 to 14. Seven is neutral and is the pH of pure water. Solutions with a pH less than seven are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than seven are basic (or alkaline).
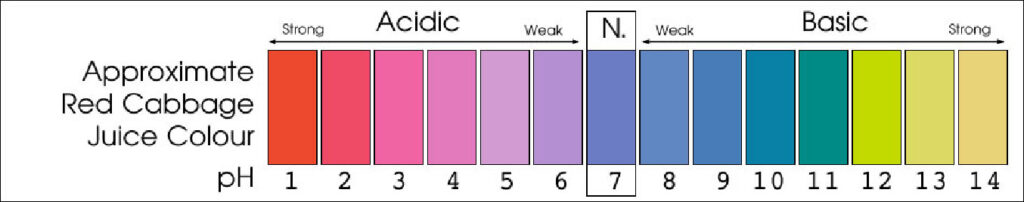
V] Further exploration.
In your experiment, lemon juice created a red-pink color while baking soda created a blue-green color. Predict what color you will see if you mixed the two solutions together,. Go ahead and mix them! What color do you see? Anything else happen?
Red cabbage makes an excellent pH indicator. Do you think other plants might make a good pH indicator? . Try making a pH indicator with other plants such as beets, blueberries, and red grapes, or?
Pollution from coal-burning power plants often lowers the pH of rain , creating acid rain, which in turn can lower the pH of lakes, streams and soil. Would a lake that has a granite bed be more susceptible to acid rain than a lake with a limestone bed? If you can, grind up some limestone or use a bag of pure garden lime, which is made of ground limestone. Mix the crushed limestone or garden lime with water and test it with your pH indicator. Does knowing the pH of the water mixed with limestone give you better understanding of what might happen when that water mixed with acid rain? What would happen if acid rain rained on a lake with a granite bed?

VII] For further study.
Why is hydrogen important in understanding pH?
Understanding pH on the molecular level is difficult to understand for most kids and even some adults. If you are curious, when you are older, you might want to take a chemistry class. However if you can’t wait, here’s a quick, simplified version that may be useful to you.
 The letters pH are an abbreviation for potential of hydrogen, which means whether or not a solution has the potential to react with other solutions by giving up or taking in hydrogen ions. An acid will react by giving up hydrogen ions, whereas a base will react by taking in hydrogen ions. Sometimes these reactions can be violent, like when mixing baking soda and vinegar.
The letters pH are an abbreviation for potential of hydrogen, which means whether or not a solution has the potential to react with other solutions by giving up or taking in hydrogen ions. An acid will react by giving up hydrogen ions, whereas a base will react by taking in hydrogen ions. Sometimes these reactions can be violent, like when mixing baking soda and vinegar.
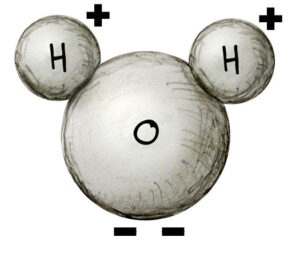
 The water molecule, H2O
The water molecule, H2O
Water is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Oxygen atoms have a negative charge while hydrogen atoms have a positive charge. Oxygen’s negative charge is twice as strong hydrogen’s positive charge, so it takes two hydrogen atoms to match the negative charge of oxygen. This balance of charges makes water neutral. Acid solutions have an abundance of positively charged hydrogen atoms which are called hydrogen ions (H+) The more H+ ions present in solution, the stronger the acid.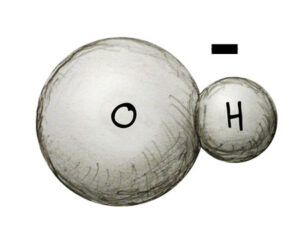
Base solutions (also called alkaline solutions) have an abundance of hydroxide ions (OH-). The bond of one hydrogen to one oxygen atom is a hydroxide ion. The more OH- ions in solution, the stronger the base.
Why does red cabbage juice change color?
Red cabbage contains the dye anthocyanin, which reacts to either hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions in a solution by changing color. This makes it a pH indicator. Its molecules are changed by a chemical reaction when they release or capture hydrogen ions. These differences also affect how anthocyanin molecules absorb different wavelengths of the color spectrum. The wavelength of light that is not absorbed gets reflected back to our eyes, the color we see. So different wavelengths of light being absorbed results in different wavelengths being reflected back to our eyes, which we see as different colors.
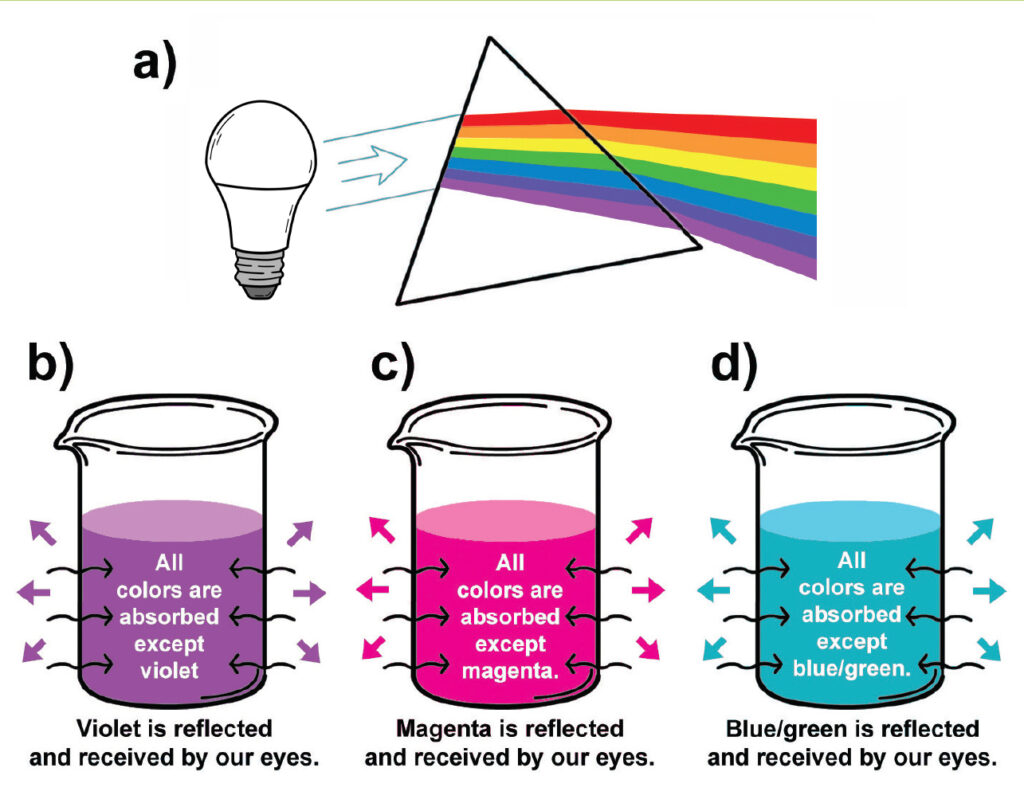
a) Visible light is separated into its individual colors by refraction through a prism.
b) All the colors of the visible spectrum are absorbed, but purple–the color we see–when light hits the dye anthocyanin in red cabbage juice.
c) All colors are absorbed but reds & pinks when anthocyanin reacts with an acid. d) All the colors are absorbed but greens & blues when anthocyanin reacts with a base.

